Matthew Dressa
Matthew Dressa
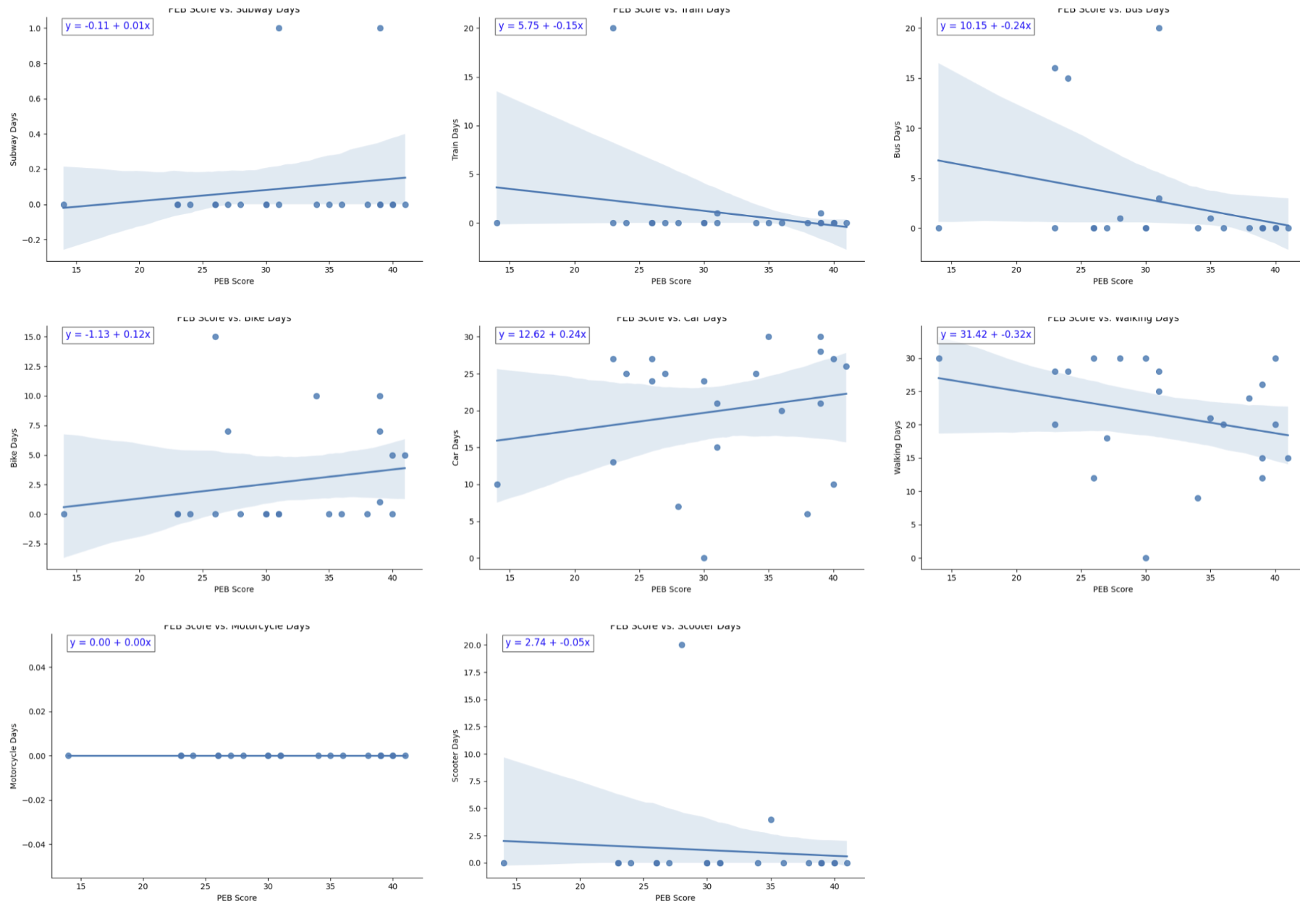
Household Perceptions on Sustainable Transportation Methods
Data ScienceBy examining how environmental knowledge and attitudes influence household transportation decisions, we sought to contribute to the development of more holistic strategies for promoting sustainable collaborative sense making interfaces for transportation. Learn More
ART_I
Human Centered DesignAI based tools have the capacity to aid creative endeavors, such as digital drawing by providing source images to use for references when drawing particular subjects and providing general inspiration. For example, models like DALL·E can generate never before seen images that would be difficult to find through search engines. However, models like DALL·E are not often used as more than a novelty, with more advanced use of these models resesrved for those with previous experience with AI. This motivated us to create an AI tool for generating novel reference images for digital artists in their creative process called ART-i. Learn More

Vibrosense: Recognizing home activities
Data Science HardwareSmart homes of the future are envisioned to have the ability to recognize many types of home activities such as running a washing machine, flushing the toilet, and using a microwave. In this paper, we present a new sensing technology, VibroSense, which is able to recognize 18 different types of activities throughout a house by observing structural vibration patterns on a wall or ceiling using a... Learn More

BodyTrak: Inferring Full-body Poses from Body Silhouettes using a Wristband
Data Science HardwareIn this paper, we present BodyTrak, the first smart wristband that can estimate the full body poses in 3D. It uses miniature cameras mounted on the wrist to capture the body silhouettes, which are learned by a customized deep learning model to estimate the 3D positions of 14 joints on arms, legs, torso, and head. We conducted a user study with 9 participants in which each participant performed 12 daily activities such as walking, sitting, or exercising, in varying scenarios (wearing different clothes, outdoors/indoors). The results show that our system can infer the full body pose (3D positions of 14 joints) with an average error of 6.89 cm and 6.34 cm, using just one camera and four cameras mounted on the wrist respectively. Based on the results... Learn More